IMPORTANT SAFETY DISCLAIMER: While this article provides educational information about homemade sunscreen formulations, it’s crucial to understand that DIY sunscreens may not provide the same level of protection as commercially tested and FDA-approved products. Always perform patch tests, consider professional sun protection for extended outdoor activities, and consult dermatologists for specific skin protection needs.
Homemade sunscreen represents a natural approach to sun protection that allows complete control over ingredients while avoiding potentially harmful chemicals found in many commercial formulations. Creating effective homemade sunscreen requires understanding the science of UV protection, selecting appropriate natural ingredients with proven SPF properties, and following proper formulation techniques to ensure adequate coverage and protection.
The growing interest in homemade sunscreen stems from concerns about chemical sunscreen ingredients like oxybenzone, octinoxate, and avobenzone, which have been linked to coral reef damage and potential health concerns. Natural alternatives using zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and plant-based ingredients offer mineral protection that sits on the skin’s surface rather than being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Understanding how to properly formulate homemade sunscreen empowers you to create customized protection that suits your skin type, activity level, and environmental concerns while maintaining effective UV defense. These natural formulations provide broad-spectrum protection through physical barrier methods that reflect and scatter harmful UV rays rather than absorbing them chemically.
Creating safe and effective homemade sunscreen requires careful attention to ingredient ratios, proper mixing techniques, and realistic expectations about protection levels. This comprehensive guide provides scientifically-informed recipes and safety protocols to help you make informed decisions about natural sun protection while understanding both the benefits and limitations of DIY formulations.
Understanding UV Protection and Homemade Sunscreen Science
The Science Behind Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
SPF ratings indicate how long skin protected by sunscreen can be exposed to UV radiation before burning compared to unprotected skin. Commercial sunscreens undergo rigorous testing to determine accurate SPF ratings, while homemade sunscreen effectiveness depends on ingredient quality, formulation precision, and application thickness, making exact SPF determination challenging but not impossible.
UV Radiation Types and Protection Needs UVA rays penetrate deeply into skin, causing premature aging and DNA damage, while UVB rays cause surface burning and immediate visible damage. Effective homemade sunscreen must provide broad-spectrum protection against both UV types through ingredients that physically block or chemically absorb these harmful radiations.
Natural SPF Ingredient Mechanisms Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide provide physical protection by creating a barrier that reflects UV rays away from skin. These minerals offer broad-spectrum protection and remain stable under sun exposure, making them ideal base ingredients for homemade sunscreen formulations that require reliable, long-lasting protection.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations for Homemade Sunscreen
Protection Level Considerations Homemade sunscreen typically provides SPF 15-30 protection when properly formulated, which is suitable for daily wear and moderate sun exposure but may be insufficient for extended outdoor activities, high-altitude environments, or individuals with very fair skin who require higher protection levels.
Application and Reapplication Requirements Effective protection from homemade sunscreen requires generous application (approximately 1/4 teaspoon for face and neck) and frequent reapplication every 2 hours or after swimming, sweating, or toweling off. These requirements are more critical with homemade formulations due to potential variations in consistency and adherence.
Testing and Quality Control Challenges Unlike commercial sunscreens that undergo standardized SPF testing, homemade sunscreen protection levels must be estimated based on ingredient percentages and proven formulation principles. This uncertainty requires conservative protection estimates and supplementary protection methods for high-risk sun exposure situations.
Natural Ingredients with Proven SPF Properties
Zinc Oxide: The Gold Standard Zinc oxide provides the highest natural SPF protection, offering broad-spectrum coverage against both UVA and UVB rays. Non-nano zinc oxide particles remain on the skin’s surface, providing immediate protection without absorption concerns, making it the preferred choice for effective homemade sunscreen formulations.
Titanium Dioxide: Secondary Protection Titanium dioxide offers good UVB protection and some UVA coverage, though less comprehensive than zinc oxide. When combined with zinc oxide in homemade sunscreen, titanium dioxide helps create broad-spectrum protection while potentially reducing the white cast associated with high zinc oxide concentrations.
Natural Oils with SPF Properties Certain plant oils provide modest natural SPF ranging from 2-8, including coconut oil (SPF 4-8), shea butter (SPF 3-4), and red raspberry seed oil (SPF 28-50 estimated). While these ingredients alone cannot provide adequate protection, they enhance homemade sunscreen formulations while providing nourishing skin benefits.
Essential Ingredients for Effective Homemade Sunscreen
Primary Active Ingredients
Non-Nano Zinc Oxide Non-nano zinc oxide (particle size larger than 100 nanometers) provides superior protection without penetrating skin barrier. Choose pharmaceutical-grade zinc oxide with particle sizes that ensure surface-level protection while maintaining effectiveness in homemade sunscreen formulations.
Titanium Dioxide Selection Select non-nano titanium dioxide specifically designed for cosmetic use to ensure safety and effectiveness in homemade sunscreen. Avoid food-grade titanium dioxide, which may not provide adequate UV protection or proper particle size distribution for sun protection applications.
Combination Ratios for Optimal Protection Effective homemade sunscreen typically contains 15-25% zinc oxide for SPF 15-30 protection. Adding 2-5% titanium dioxide can enhance broad-spectrum coverage while potentially reducing the visible white cast, though zinc oxide remains the primary protective ingredient.
Base and Carrier Ingredients
Oil Phase Components Coconut oil, jojoba oil, and olive oil provide excellent bases for homemade sunscreen, offering easy application, skin nourishment, and natural preservation properties. These oils help create smooth, spreadable formulations while contributing modest additional SPF protection.
Emulsifying and Stabilizing Agents Beeswax, candelilla wax, and shea butter provide structure and water resistance to homemade sunscreen while creating stable emulsions that maintain ingredient distribution. Proper wax content ensures the formulation stays blended and provides adequate coverage during application.
Natural Preservation and Stability Vitamin E oil, rosemary extract, and grapefruit seed extract help preserve homemade sunscreen and prevent rancidity while maintaining ingredient integrity. These natural preservatives extend shelf life and maintain effectiveness without synthetic additives.
Enhancement and Comfort Ingredients
Skin-Soothing Additives Aloe vera gel, chamomile extract, and calendula oil provide anti-inflammatory benefits that soothe sun-exposed skin while enhancing the comfort of homemade sunscreen application. These ingredients also help reduce potential irritation from mineral UV filters.
Application Enhancement Lecithin and natural emulsifiers improve the spreadability and application of homemade sunscreen while reducing the white cast associated with mineral UV filters. These ingredients help create smoother, more cosmetically elegant formulations.
Antioxidant Protection Green tea extract, vitamin C, and other natural antioxidants provide additional protection against free radical damage from UV exposure while supporting skin health and potentially enhancing the protective properties of homemade sunscreen formulations.
10 Ultimate Homemade Sunscreen Recipes
Recipe #1: Basic Daily Protection Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 15-20 Perfect for: Daily wear, moderate sun exposure, sensitive skin Benefits: Simple formulation, gentle ingredients, easy application
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup coconut oil
- 2 tablespoons shea butter
- 2 tablespoons beeswax pellets
- 2 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 10 drops lavender essential oil (optional)
Instructions:
- Melt coconut oil, shea butter, and beeswax in double boiler
- Remove from heat and let cool slightly
- Whisk in zinc oxide powder gradually to prevent clumping
- Add vitamin E oil and essential oil if using
- Pour into clean containers while still liquid
- Allow to cool completely before use
- Apply generously and reapply every 2 hours
This basic homemade sunscreen provides reliable daily protection through a simple, gentle formulation suitable for most skin types. The combination of nourishing oils and mineral protection creates an effective barrier against UV damage while maintaining skin comfort.
Recipe #2: Water-Resistant Sport Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 20-25 Perfect for: Athletic activities, swimming, high-sweat situations Benefits: Enhanced water resistance, stronger protection, active lifestyle suitable
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup coconut oil
- 2 tablespoons cocoa butter
- 3 tablespoons beeswax pellets
- 3 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon jojoba oil
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 5 drops peppermint essential oil
Instructions:
- Melt coconut oil, cocoa butter, and beeswax completely
- Cool slightly while maintaining liquid state
- Slowly whisk in zinc oxide to ensure even distribution
- Add jojoba oil and vitamin E oil
- Include peppermint oil for cooling sensation
- Pour into waterproof containers
- Test water resistance before relying on for swimming
This sport-formulated homemade sunscreen provides enhanced protection and water resistance through increased wax content and higher zinc oxide concentration, making it suitable for active outdoor pursuits while maintaining effective UV protection.
Recipe #3: Sensitive Skin Gentle Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 15 Perfect for: Sensitive skin, children, reactive skin types Benefits: Minimal ingredients, hypoallergenic, gentle protection
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup olive oil
- 2 tablespoons shea butter
- 1 tablespoon beeswax pellets
- 2 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon aloe vera gel
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
Instructions:
- Gently melt olive oil, shea butter, and beeswax
- Remove from heat and cool to room temperature
- Gradually incorporate zinc oxide with gentle whisking
- Blend in aloe vera gel and vitamin E oil
- Mix thoroughly to ensure smooth consistency
- Store in clean, air-tight containers
- Perform patch test before full application
This gentle homemade sunscreen formulation minimizes potential irritants while providing effective protection for sensitive skin types. The simple ingredient list reduces allergy risk while maintaining adequate UV protection through proven mineral ingredients.
Recipe #4: Anti-Aging Enhanced Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 20-25 Perfect for: Mature skin, anti-aging focus, daily facial protection Benefits: Antioxidant enhancement, age-prevention focus, skin nourishment
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup argan oil
- 2 tablespoons shea butter
- 2 tablespoons beeswax pellets
- 3 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon rosehip seed oil
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 5 drops frankincense essential oil
- 1 teaspoon green tea extract
Instructions:
- Melt argan oil, shea butter, and beeswax gently
- Cool mixture to warm but not hot temperature
- Whisk in zinc oxide powder thoroughly
- Add rosehip seed oil and vitamin E oil
- Incorporate green tea extract and essential oil
- Blend until completely smooth and uniform
- Package in dark containers to preserve antioxidants
This anti-aging focused homemade sunscreen combines effective UV protection with powerful antioxidants and age-fighting ingredients to provide comprehensive protection against both immediate and long-term sun damage while nourishing mature skin.
Recipe #5: Tinted Homemade Sunscreen for Face
SPF Level: Approximately 15-20 Perfect for: Facial application, light coverage, daily makeup base Benefits: Natural tinting, face-specific formulation, cosmetic elegance
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup jojoba oil
- 2 tablespoons shea butter
- 1 tablespoon beeswax pellets
- 2 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 teaspoon cocoa powder (for tinting)
- 1 teaspoon arrowroot powder
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 3 drops geranium essential oil
Instructions:
- Melt jojoba oil, shea butter, and beeswax carefully
- Cool to warm temperature before adding powders
- Sift zinc oxide and cocoa powder to remove lumps
- Gradually whisk in powdered ingredients
- Add arrowroot powder for smooth application
- Include vitamin E oil and essential oil
- Adjust cocoa powder for desired tint level
This tinted homemade sunscreen provides facial protection with natural color enhancement, creating a makeup base that protects while providing light coverage and improving skin appearance throughout sun exposure.
Recipe #6: High-Protection Beach Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 25-30 Perfect for: Beach activities, intense sun exposure, tropical climates Benefits: Maximum homemade protection, water resistance, tropical formula
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup coconut oil
- 3 tablespoons cocoa butter
- 3 tablespoons beeswax pellets
- 4 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon titanium dioxide (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon red raspberry seed oil
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 5 drops eucalyptus essential oil
Instructions:
- Melt coconut oil, cocoa butter, and beeswax completely
- Allow to cool while maintaining workable consistency
- Slowly incorporate zinc oxide and titanium dioxide
- Add red raspberry seed oil for additional SPF
- Include vitamin E oil and eucalyptus oil
- Mix thoroughly to ensure even mineral distribution
- Package in travel-friendly, waterproof containers
This high-protection homemade sunscreen provides maximum DIY sun protection through increased mineral content and water-resistant formulation, making it suitable for intense sun exposure situations like beach vacations and tropical climates.
Recipe #7: Quick Application Spray Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 15 Perfect for: Easy application, body coverage, convenient reapplication Benefits: Spray application, lightweight feel, easy reapplication
Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup aloe vera gel
- 1/4 cup witch hazel
- 2 tablespoons fractionated coconut oil
- 2 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (micronized, non-nano)
- 1 teaspoon lecithin
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 10 drops lavender essential oil
Instructions:
- Combine aloe vera gel with witch hazel in spray bottle
- Add fractionated coconut oil and lecithin
- Shake vigorously to create initial emulsion
- Gradually add zinc oxide while shaking continuously
- Include vitamin E oil and essential oil
- Shake well before each use
- Spray evenly and rub in for complete coverage
This spray formulation of homemade sunscreen provides convenient application for large body areas while maintaining effective protection through properly dispersed mineral ingredients in a lightweight, easy-to-apply format.
Recipe #8: Lip Protection Homemade Sunscreen Balm
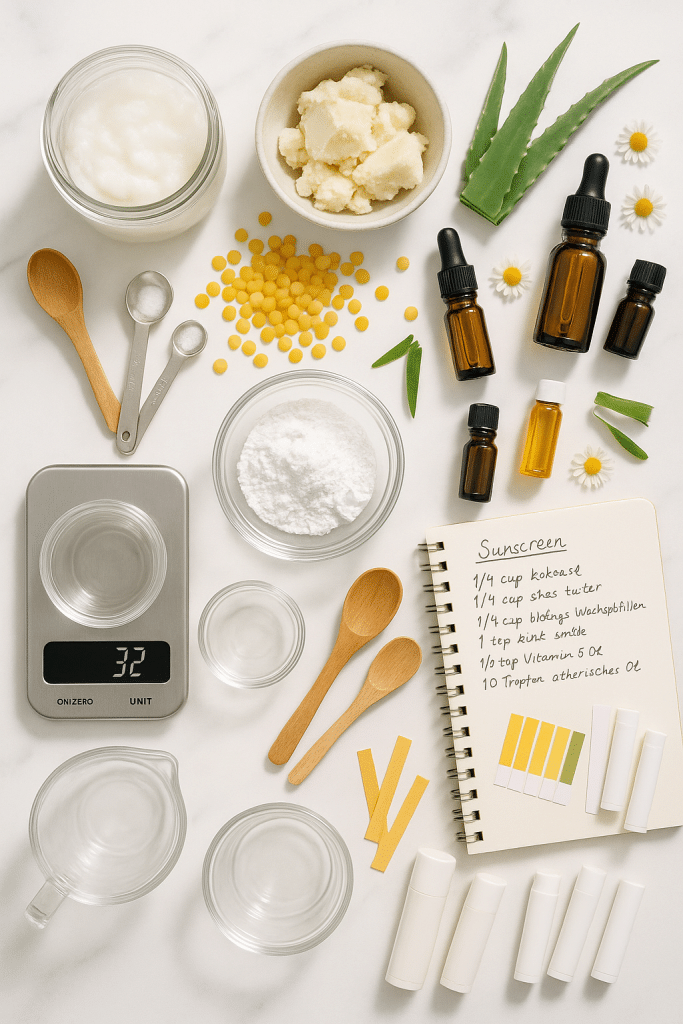
Homemade sunscreen natural ingredients and finished products arranged for DIY sun protection routine
SPF Level: Approximately 15-20 Perfect for: Lip protection, facial stick application, targeted coverage Benefits: Convenient stick format, lip-safe ingredients, portable protection
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons coconut oil
- 1 tablespoon beeswax pellets
- 1 tablespoon shea butter
- 1 tablespoon zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 3 drops peppermint essential oil (optional)
Instructions:
- Melt coconut oil, beeswax, and shea butter gently
- Remove from heat and cool slightly
- Whisk in zinc oxide powder thoroughly
- Add vitamin E oil and peppermint oil if using
- Pour into lip balm tubes or small containers
- Allow to solidify completely before use
- Apply generously to lips and reapply frequently
This lip-specific homemade sunscreen provides targeted protection for the delicate lip area through a convenient balm format that combines effective UV protection with nourishing ingredients safe for oral contact.
Recipe #9: After-Sun Repair Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 15 Perfect for: Sun-damaged skin, post-exposure care, healing support Benefits: Healing ingredients, soothing properties, protective repair
Ingredients:
- 1/4 cup aloe vera gel
- 2 tablespoons coconut oil
- 1 tablespoon beeswax pellets
- 2 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1 tablespoon calendula oil
- 1 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 5 drops lavender essential oil
- 1 teaspoon honey
Instructions:
- Gently melt coconut oil and beeswax
- Cool to warm temperature
- Blend in aloe vera gel and honey
- Gradually incorporate zinc oxide powder
- Add calendula oil and vitamin E oil
- Include lavender oil for healing properties
- Apply to sun-exposed skin for protection and repair
This healing-focused homemade sunscreen combines protective ingredients with skin-repairing compounds to provide both ongoing protection and therapeutic benefits for sun-damaged or sensitive skin requiring gentle care.
Recipe #10: Travel-Size Compact Homemade Sunscreen
SPF Level: Approximately 20 Perfect for: Travel convenience, purse-friendly, quick touch-ups Benefits: Compact format, TSA-friendly, portable protection
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons coconut oil
- 1 tablespoon shea butter
- 1 tablespoon beeswax pellets
- 1.5 tablespoons zinc oxide powder (non-nano)
- 1/2 teaspoon vitamin E oil
- 3 drops tea tree essential oil
Instructions:
- Melt coconut oil, shea butter, and beeswax
- Cool to workable temperature
- Whisk in zinc oxide powder completely
- Add vitamin E oil and essential oil
- Pour into small, portable containers (1 oz or less)
- Label with ingredients and SPF estimate
- Carry for convenient reapplication during travel
This compact homemade sunscreen formulation provides effective protection in a travel-friendly format that meets airline regulations while ensuring sun protection availability during trips and daily activities.
Safety Guidelines and Best Practices for Homemade Sunscreen
Ingredient Safety and Quality Control
Source Quality Verification Purchase zinc oxide and titanium dioxide from reputable cosmetic ingredient suppliers to ensure particle size, purity, and safety standards appropriate for topical application. Avoid industrial-grade minerals that may contain contaminants or inappropriate particle sizes for skin contact.
Non-Nano Particle Selection Choose non-nano zinc oxide and titanium dioxide (particles larger than 100 nanometers) to ensure minerals remain on skin surface rather than penetrating into deeper tissue layers. This selection provides effective protection while minimizing potential absorption concerns.
Contamination Prevention Use sterile equipment, clean containers, and fresh ingredients when preparing homemade sunscreen to prevent bacterial contamination that could cause skin infections or product degradation. Replace ingredients that show signs of rancidity or contamination.
Application and Usage Protocols
Proper Application Amounts Apply homemade sunscreen generously using approximately 1/4 teaspoon for face and neck, with proportional amounts for body coverage. Insufficient application dramatically reduces protection effectiveness, making generous application crucial for adequate UV protection.
Reapplication Requirements Reapply homemade sunscreen every 2 hours or immediately after swimming, sweating, or toweling off to maintain protection levels. Natural formulations may have shorter effective duration than commercial products, making frequent reapplication essential.
Activity-Appropriate Selection Choose appropriate homemade sunscreen formulations based on planned activities, with water-resistant formulas for swimming and higher SPF recipes for intense sun exposure. Match protection level to actual sun exposure risk for optimal safety.
Testing and Patch Testing Protocols
Skin Sensitivity Assessment Perform patch tests on small skin areas 24-48 hours before full application of new homemade sunscreen formulations to identify potential allergic reactions or skin sensitivities. Discontinue use if irritation, redness, or discomfort occurs.
Protection Level Verification Test homemade sunscreen protection through gradual sun exposure increases while monitoring skin response. Start with short exposure periods and increase gradually while observing for any signs of burning or damage.
Formulation Consistency Evaluation Assess homemade sunscreen consistency, spreadability, and coverage uniformity to ensure adequate protection distribution. Reformulate if the product separates, becomes too thick, or doesn’t spread evenly across skin surface.
Understanding Limitations and Professional Alternatives
When to Use Commercial Sunscreen
High-Risk Situations Consider commercial broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreens for extended outdoor activities, high-altitude exposure, tropical climates, or individuals with fair skin requiring maximum protection that exceeds typical homemade sunscreen capabilities.
Medical Conditions and Medications Individuals with photosensitive medical conditions, those taking photosensitizing medications, or people with history of skin cancer should consult dermatologists about appropriate sun protection rather than relying solely on homemade sunscreen formulations.
Professional Activity Requirements Occupations requiring extended outdoor work may necessitate commercial sunscreens with verified SPF ratings and water resistance testing to ensure adequate protection throughout long work periods in variable conditions.
Regulatory and Testing Considerations
FDA Approval Differences Commercial sunscreens undergo standardized SPF testing and FDA approval processes that homemade sunscreen cannot replicate, creating inherent uncertainty about exact protection levels despite careful formulation using proven ingredients.
Professional Testing Options Some laboratories offer SPF testing services for custom formulations, though costs may be prohibitive for personal use. These tests can provide accurate protection data for those requiring verified SPF ratings.
Legal and Liability Considerations Understand that homemade sunscreen use carries personal responsibility for protection adequacy, and sharing formulations with others may involve liability considerations if inadequate protection results in sun damage.
Complementary Protection Strategies
Physical Protection Integration Combine homemade sunscreen with physical protection methods including wide-brimmed hats, UV-protective clothing, and shade-seeking to create comprehensive sun protection strategies that don’t rely solely on topical products.
Timing and Avoidance Strategies Plan outdoor activities during lower UV intensity periods (before 10 AM and after 4 PM) to reduce overall sun exposure and reliance on sunscreen protection during peak UV radiation hours.
Skin Health Support Support overall skin health through antioxidant-rich diets, adequate hydration, and skin-nourishing practices that enhance natural UV resistance while maintaining realistic expectations about homemade sunscreen protection capabilities.
Troubleshooting Common Homemade Sunscreen Issues
Texture and Application Problems
White Cast Reduction Minimize white cast from zinc oxide through proper particle size selection, adequate blending, and consideration of tinted formulations or zinc oxide alternatives like titanium dioxide combinations that may provide less visible coverage.
Consistency Adjustments Modify homemade sunscreen consistency through oil and wax ratio adjustments, with more oils for easier spreading and additional wax for firmer consistency. Temperature during application also affects spreadability and coverage uniformity.
Separation and Stability Issues Address formulation separation through proper emulsifier selection, adequate mixing during preparation, and appropriate storage conditions. Some separation may be normal and can be resolved through remixing before application.
Protection and Effectiveness Concerns
Coverage Assessment Ensure adequate coverage through systematic application patterns and generous product amounts. Missed areas and thin application significantly reduce protection effectiveness, making thorough coverage crucial for homemade sunscreen success.
Duration and Reapplication Monitor protection duration through careful sun exposure observation and establish reapplication schedules based on activity level, sweating, and environmental conditions rather than relying on time alone.
Environmental Factors Consider environmental factors like altitude, water reflection, and seasonal UV intensity changes that may require homemade sunscreen formulation adjustments or supplementary protection methods for adequate coverage.
Storage and Preservation Challenges
Shelf Life Management Monitor homemade sunscreen for signs of rancidity, separation, or contamination and establish reasonable shelf life expectations (typically 3-6 months) based on ingredient stability and storage conditions.
Temperature Stability Understand that homemade sunscreen may soften in heat or harden in cold, requiring temperature-appropriate storage and potential reformulation for extreme climate conditions or seasonal use variations.
Contamination Prevention Implement contamination prevention through clean application methods, proper storage containers, and avoiding direct finger contact with product containers to maintain homemade sunscreen quality throughout use period.
Advanced Formulation Techniques
Emulsification and Stability Enhancement
Natural Emulsifier Selection Improve homemade sunscreen stability through natural emulsifiers like lecithin, ewax, or polysugarcane that help bind oil and water phases while maintaining ingredient integrity and improving application characteristics.
pH Optimization Monitor and adjust homemade sunscreen pH levels to optimize ingredient stability and skin compatibility, using natural pH adjusters like citric acid or baking soda to maintain appropriate acidity levels for skin health.
Antioxidant Preservation Include natural antioxidants like vitamin E, rosemary extract, or grapefruit seed extract to prevent rancidity and extend homemade sunscreen shelf life while maintaining active ingredient effectiveness over time.
Customization and Enhancement Strategies
Climate-Specific Formulations Develop climate-specific homemade sunscreen formulations with lighter consistency for humid environments and richer formulations for dry climates to optimize protection and comfort across different environmental conditions.
Skin Type Adaptations Customize homemade sunscreen for different skin types through ingredient selection, with lighter oils for oily skin and richer formulations for dry skin while maintaining effective UV protection across all variations.
Activity-Specific Modifications Create activity-specific homemade sunscreen formulations with enhanced water resistance for swimming, lighter formulations for daily wear, and higher protection levels for intense outdoor activities.
Quality Control and Testing Methods
Consistency Monitoring Establish quality control protocols for homemade sunscreen including visual inspection, consistency testing, and documentation of formulation changes to ensure reliable protection across different batches.
Protection Verification Develop personal testing protocols for homemade sunscreen effectiveness through controlled sun exposure and skin response monitoring while maintaining safety and avoiding overexposure risks.
Improvement Documentation Document homemade sunscreen formulation improvements, application observations, and protection effectiveness to refine recipes and enhance protection over time through systematic evaluation.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Reef-Safe Formulations
Coral-Friendly Ingredients Choose coral reef-safe ingredients for homemade sunscreen by avoiding oxybenzone, octinoxate, and other chemicals known to harm marine ecosystems. Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide provide effective protection without environmental damage.
Biodegradable Components Select biodegradable oils and natural ingredients for homemade sunscreen to minimize environmental impact when swimming or through runoff, supporting marine ecosystem health while maintaining personal sun protection.
Packaging Sustainability Use sustainable packaging options for homemade sunscreen including glass containers, metal tins, or recyclable materials to reduce plastic waste and support environmental protection goals alongside personal health priorities.
Chemical Exposure Reduction
Synthetic Ingredient Avoidance Eliminate exposure to synthetic sunscreen chemicals through homemade sunscreen formulations using only natural, mineral-based ingredients that provide physical UV protection without systemic absorption concerns.
Endocrine Disruptor Prevention Avoid potential endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in some commercial sunscreens through careful ingredient selection in homemade sunscreen, choosing only ingredients with established safety profiles for topical use.
Allergen Minimization Reduce allergic reaction risks through simple homemade sunscreen formulations using minimal, well-tolerated ingredients and avoiding common allergens or sensitizing compounds found in commercial products.
Sustainable Beauty Integration
Zero-Waste Practices Integrate homemade sunscreen into zero-waste beauty routines through bulk ingredient purchasing, reusable containers, and minimal packaging approaches that support environmental sustainability goals.
Seasonal Ingredient Use Utilize seasonal ingredients when available for homemade sunscreen enhancement, supporting local agriculture and reducing transportation impact while maintaining effective sun protection throughout the year.
Community Sharing Share homemade sunscreen knowledge and ingredients with community members to support collective environmental health and reduce reliance on commercial products with potentially harmful environmental impacts.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
Ingredient Investment and Long-Term Savings
Initial Cost Breakdown Initial investment in homemade sunscreen ingredients typically ranges from $40-80, providing materials for 15-25 batches compared to commercial sunscreen costs of $8-25 per bottle, creating substantial long-term savings.
Per-Application Cost Analysis Homemade sunscreen costs approximately $0.75-1.50 per application compared to $1.50-4.00 for equivalent commercial products, resulting in 50-70% cost savings with proper formulation and application techniques.
Quality Enhancement Value Homemade sunscreen often provides superior ingredient quality through organic, non-nano mineral selection and pure base ingredients compared to commercial products with fillers, preservatives, and synthetic additives.
Bulk Purchasing and Sourcing Strategies
Ingredient Bulk Benefits Purchase homemade sunscreen ingredients in bulk quantities to reduce per-unit costs while ensuring adequate supplies for consistent sun protection throughout peak sun exposure seasons.
Quality Source Identification Identify reliable, quality sources for homemade sunscreen ingredients including cosmetic suppliers, health food stores, and online retailers specializing in natural skincare ingredients.
Seasonal Cost Optimization Time ingredient purchases for homemade sunscreen preparation to take advantage of seasonal sales and availability cycles while ensuring adequate supplies for upcoming sun exposure periods.
Value-Added Benefits
Multi-Purpose Ingredient Utility Choose ingredients for homemade sunscreen that serve multiple purposes in natural beauty and health routines to maximize investment value and utility across different applications.
Customization Value Factor in customization value of homemade sunscreen that provides specific formulations for individual skin types, preferences, and protection needs impossible with commercial one-size-fits-all products.
Health Investment Perspective Consider homemade sunscreen as health investment that provides both immediate sun protection and long-term benefits through reduced chemical exposure and enhanced skin health support.
Seasonal Adaptations and Year-Round Protection
Spring and Summer Formulations
High-UV Season Preparations Develop stronger homemade sunscreen formulations for spring and summer months when UV intensity increases, using higher zinc oxide concentrations and water-resistant bases for enhanced protection during peak seasons.
Heat Stability Considerations Formulate homemade sunscreen with heat stability in mind for summer use, adjusting wax content and base oils to maintain proper consistency in high temperatures while preserving protection effectiveness.
Activity-Specific Summer Recipes Create specialized homemade sunscreen formulations for summer activities including beach formulas with maximum protection, sport formulas with enhanced water resistance, and daily formulas for routine summer protection.
Fall and Winter Adaptations
Lower UV Maintenance Adjust homemade sunscreen formulations for fall and winter months with lighter protection levels while maintaining daily UV defense against year-round sun exposure, particularly from snow reflection and high-altitude activities.
Moisturizing Enhancement Increase moisturizing components in winter homemade sunscreen formulations to address dry air and harsh weather effects while providing necessary UV protection during outdoor winter activities.
Indoor-Outdoor Transition Develop transitional homemade sunscreen formulations for fall and winter that provide adequate protection for brief outdoor exposure while supporting skin health during lower UV seasons.
Climate-Specific Formulations
Tropical Climate Adaptations Create specialized homemade sunscreen formulations for tropical climates with maximum protection, enhanced water resistance, and stability in high heat and humidity conditions.
Arid Climate Modifications Adjust homemade sunscreen for arid climates through increased moisturizing components and dust-resistant formulations that maintain protection in dry, windy conditions with high UV reflection.
Temperate Climate Balance Develop balanced homemade sunscreen formulations for temperate climates that provide adequate protection across seasonal variations while maintaining comfort and effectiveness year-round.
Professional Integration and Expert Consultation
Dermatologist Collaboration
Professional Assessment Consult dermatologists about homemade sunscreen use, particularly for individuals with skin conditions, cancer history, or specific protection requirements that may necessitate commercial products with verified SPF ratings.
Skin Type Professional Evaluation Work with skincare professionals to assess individual skin type, photosensitivity, and protection needs to determine appropriate homemade sunscreen formulations and supplementary protection strategies.
Monitoring and Adjustment Establish professional monitoring protocols for homemade sunscreen use to ensure adequate protection and identify any signs of inadequate coverage or skin damage requiring formulation adjustments.
Integration with Professional Treatments
Chemical Peel and Procedure Coordination Coordinate homemade sunscreen use with professional skincare treatments that increase photosensitivity, ensuring adequate protection during healing periods when enhanced sun protection is crucial.
Medical Treatment Compatibility Verify homemade sunscreen ingredient compatibility with medical treatments and medications that may affect skin sensitivity or interact with topical ingredients used in natural formulations.
Professional Product Combination Consider combining homemade sunscreen with professional sun protection products for high-risk situations while maintaining daily natural protection for routine sun exposure.
Educational Resources and Continued Learning
Scientific Literature Review Stay current with scientific research on natural sun protection ingredients and UV protection mechanisms to improve homemade sunscreen formulations based on emerging evidence and best practices.
Professional Development Pursue education in cosmetic formulation, dermatology, and sun protection science to enhance homemade sunscreen creation skills and safety protocols for optimal protection results.
Community Learning Networks Participate in communities focused on natural skincare and homemade cosmetics to share knowledge, troubleshoot formulation challenges, and discover new techniques for effective homemade sunscreen creation.
Conclusion: Embracing Natural Sun Protection Through Homemade Sunscreen
Creating effective homemade sunscreen represents a meaningful step toward natural, sustainable sun protection that puts you in complete control of ingredients while providing reliable UV defense for daily activities and moderate sun exposure. Through careful formulation, proper application, and realistic expectations, homemade sunscreen can serve as an excellent foundation for comprehensive sun protection strategies.
The journey toward natural sun protection through homemade sunscreen requires commitment to learning, experimentation, and safety protocols that ensure adequate protection while enjoying the benefits of chemical-free, customizable formulations. Each recipe in this guide provides a starting point for developing personalized sun protection that matches your skin type, lifestyle, and environmental values.
Success with homemade sunscreen depends on understanding both its capabilities and limitations, using appropriate formulations for specific situations, and complementing topical protection with physical barriers and smart sun exposure practices. This comprehensive approach creates reliable protection while supporting overall skin health through natural ingredients.
Remember that homemade sunscreen effectiveness relies heavily on proper application, generous coverage, and frequent reapplication just like commercial products. The natural ingredients provide gentle, effective protection when used correctly, but require the same diligent application practices as any sun protection product to maintain adequate coverage.
Long-term benefits of homemade sunscreen extend beyond immediate sun protection to include reduced chemical exposure, environmental protection, cost savings, and the satisfaction of creating personalized skincare products that align with your health and environmental values. These cumulative benefits make the learning investment worthwhile for committed natural beauty enthusiasts.
As you develop your homemade sunscreen skills, continue monitoring your skin’s response, adjusting formulations based on effectiveness, and staying informed about new research and techniques that can improve your natural sun protection strategies. This ongoing development ensures optimal protection and satisfaction with your natural approach.
The environmental benefits of choosing homemade sunscreen over chemical commercial products contribute to coral reef protection, reduced packaging waste, and decreased chemical runoff that affects marine ecosystems. Your personal choices support broader environmental health while providing effective personal protection.
Consider homemade sunscreen as one component of a comprehensive natural beauty routine that prioritizes ingredient transparency, environmental responsibility, and personal health. This integration supports holistic wellness approaches that benefit both individual health and environmental sustainability.
Start your homemade sunscreen journey with appropriate recipes for your skin type and protection needs, always prioritizing safety through proper testing and realistic protection expectations. Your commitment to natural sun protection contributes to both personal health and environmental protection while providing effective, customizable UV defense.
Embrace the empowerment that comes from understanding and creating your own sun protection while maintaining realistic expectations about protection levels and appropriate use situations. Homemade sunscreen offers valuable benefits when properly formulated and applied, supporting natural beauty goals and environmental values through effective, sustainable sun protection.
Related Articles:
- DIY Hair Masks for Damaged Hair Recovery: 15 Ultimate Recipes for Amazing Transformation
- Apple Cider Vinegar Rinses: 12 Ultimate Benefits and Amazing Hair Transformation Guide
- Overnight Beauty Treatments: 10 Ultimate DIY Recipes for Amazing Skin Transformation
External Resources:
- American Academy of Dermatology – Sunscreen Guidelines – Professional sun protection recommendations and safety guidelines
- Environmental Working Group’s Guide to Sunscreens – Independent sunscreen safety ratings and ingredient analysis
- FDA Sunscreen Regulations and Safety – Official regulatory information on sunscreen safety and effectiveness

